 The Liver
The Liver
 The liver, the largest organ in the body, is located below the diaphragm
in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity, it is sheltered by
the rib cage. In an adult, the liver normally weights about 3 pounds and
extends approximately from the right fifth rib to the lower border of the
rib cage (along an imaginary line extending down from the middle of the
collar bone). When the patient inhales, the liver edge may be felt 1 to
2 cm below the right edge of the rib cage. Liver structure has several
unique aspects. This section discusses its
The liver, the largest organ in the body, is located below the diaphragm
in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity, it is sheltered by
the rib cage. In an adult, the liver normally weights about 3 pounds and
extends approximately from the right fifth rib to the lower border of the
rib cage (along an imaginary line extending down from the middle of the
collar bone). When the patient inhales, the liver edge may be felt 1 to
2 cm below the right edge of the rib cage. Liver structure has several
unique aspects. This section discusses its
gross anatomy and blood
supply, its cellular organization, and its capacity to regenerate.






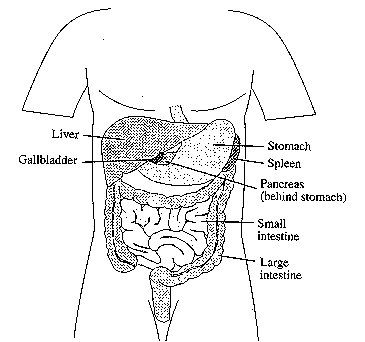
 The
liver is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal
The
liver is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal
cavity and comprises right and left lobes.
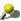 The liver receives a unique dual blood supply: systemic (body) via
The liver receives a unique dual blood supply: systemic (body) via
the hepatic artery and portal (gut) via the portal vein.
 Microscopically,
the liver is organized into structural units, or
Microscopically,
the liver is organized into structural units, or
lobules, with six peripheral portal triads and a central vein.
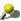 One
of the unique capacities of the liver is its ability to regenerate
One
of the unique capacities of the liver is its ability to regenerate
after partial removal or damage, although severe damage can lead to
irreversible scarring.
 The
liver is important in the synthesis and secretion of key proteins
The
liver is important in the synthesis and secretion of key proteins
(such as albumin and blood clotting proteins) and the storage of
glucose and many vitamins and minerals.
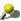 Bile, which is important for the digestion and absorption of fats, is
Bile, which is important for the digestion and absorption of fats, is
synthesized by the liver and enters the intestine via the bile ducts.
 The
liver plays a major role in the purification, transformation, and
The
liver plays a major role in the purification, transformation, and
clearance of waste products (such as ammonia), drugs, and toxins.

 Functions
Functions
 Gross
anatomy
Gross
anatomy
 Hepatic
Circulation
Hepatic
Circulation
 Regenerative
Capacity
Regenerative
Capacity




 TOP
TOP
 The Liver
The Liver
 The liver, the largest organ in the body, is located below the diaphragm
in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity, it is sheltered by
the rib cage. In an adult, the liver normally weights about 3 pounds and
extends approximately from the right fifth rib to the lower border of the
rib cage (along an imaginary line extending down from the middle of the
collar bone). When the patient inhales, the liver edge may be felt 1 to
2 cm below the right edge of the rib cage. Liver structure has several
unique aspects. This section discusses its
The liver, the largest organ in the body, is located below the diaphragm
in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity, it is sheltered by
the rib cage. In an adult, the liver normally weights about 3 pounds and
extends approximately from the right fifth rib to the lower border of the
rib cage (along an imaginary line extending down from the middle of the
collar bone). When the patient inhales, the liver edge may be felt 1 to
2 cm below the right edge of the rib cage. Liver structure has several
unique aspects. This section discusses its

